Lung Disease Research Using the iEM Platform
Since its first introduction into biomedical research, electron microscopy (EM) has become a valuable tool for the exploration of the lung"s delicate ultrastructure. It not only has demonstrated the existence of a continuous alveolar epithelium but also the presence of a surfactant lining layer. Detailed structural investigations of the alveolar septum have had a profound impact on our current physiological understanding of the lung. Creative Biostructure is a company driven by innovation, quality and technology solutions. We have established a unique integrated EM platform that can help researchers investigate lung tissues and related diseases at a nanometer scale.
Electron Microscopy (EM) in Lung
The fine ultrastructure, that is, endothelial and alveolar epithelial type 1 (AE1) cells outside the nucleus are reduced to thin extensions of cytoplasm on the capillary surface and alveolar surface respectively, achieving a thin structure of the blood-air barrier and thus ensuring efficient gas exchange. In addition, the space between the cells can be reduced to a fused basal membrane, resulting in minimal barrier thickness in the body. These structures make some requirements for the structural examination of alveolar septa. EM is a powerful method to provide images for analysis of ultrastructural pathologic changes in various tissues. Today, various EM methods have been applied to study the fine structure of the lung.
Lung Disease Research at the iEM Platform
- Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) can provide high-resolution images and is able to visualize small intra- and extracellular structures, including cell organelles, cellular inclusions, microfilaments, and collagen. Serial sectioning transmission electron microscopy (ssTEM) can achieve 3D image analysis through consecutive thin sections prepared with a routine ultramicrotome and imaged with a conventional TEM. Based on this technology, we can help researchers investigate lung research covering various topics and species. The species include humans and other animals (e.g. mice and rabbits).
- Scanning electron microscopy/ energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM/EDS)
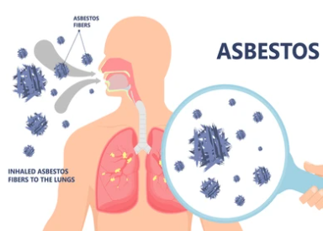
Scanning electron microscopy/ energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM/EDS) has become a useful tool for asbestos nanofibers and nanoparticles in diffuse lung diseases or lung cancer. EM is applied to quantify mineral fibers and particles in lung tissues or in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and also detect detailed elements by X-ray analytical EM. Using SEM/EDS, we are able to provide nano-scale resolution images of asbestos nanofibers and nanoparticles in histological lung specimens. We can assist researchers to investigate the relationship between bioaccumulation of asbestos nanofibers and the development of lung diseases.
Applications of Our Services
- Collect highly detailed data in vivo, involving alveolar epithelial cells, connective tissue fibers, interalveolar pores and so on.
- Evaluation and development of therapeutic approaches.
- Pathological evaluation of animal models of various lung diseases.
Thanks for your interest in our platform and solutions. We are always open to your questions and are happy to support you. contact us and our professional team or business partners will get back to you as soon as possible.
- Schneider, J. P., et al. (2020). "Volume electron microscopy: analyzing the lung." Histochemistry and Cell Biology, 1-20.

