Blood Cell Imaging Using the iEM Platform
Regular blood examinations are performed to assess general health, diagnose blood disorders and monitor the course of certain diseases. Blood cells, including red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes) are the functional components of blood. The study of blood cells is of great significance in many aspects, such as morphology, physiology, clinicopathology, and therapy. Electron microscopy(EM) has been demonstrated as an excellent tool and has been used to observe and analyze various blood cells.
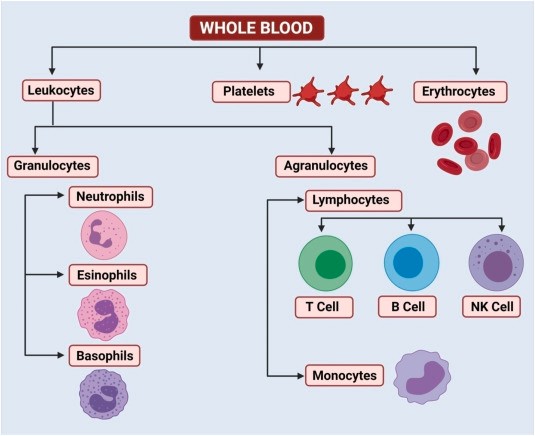 Fig.1 Diagrammatic representation of various blood cells in the humans and animals. (Choudhary, O. P., et al, 2021)
Fig.1 Diagrammatic representation of various blood cells in the humans and animals. (Choudhary, O. P., et al, 2021)
Blood Cell Imaging at the iEM Platform
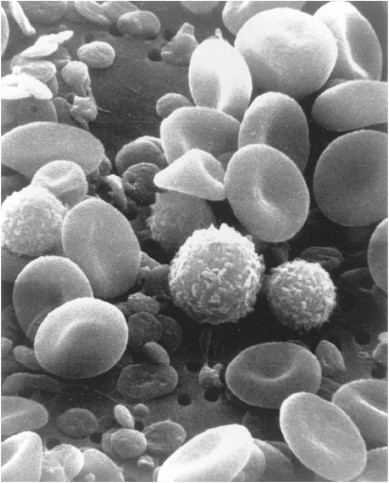 Fig2. Various blood cells under a scanning
Fig2. Various blood cells under a scanning
electron microscope. (Choudhary, O. P., et al, 2021)
At the iEM Platform, an integrated EM platform built by Creative Biostructure, researchers can investigate the blood sample surface morphology at relatively high resolution by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM), and can also gain insight into the ultrastructure of blood cells by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Our services are flexible and customized, specifically including EM blood sample preparation, RBC sample preparation, EM imaging, data acquisition and processing, structural analysis.
- Red blood cell imaging
- White blood cell imaging
- Platelet imaging
As the most abundant cell type in the human body( roughly 40-50% of the volume of the blood), red blood cells (RBCs) are primarily responsible for transporting nutrients and gases to the body. Their essential functions depend largely on the unique shape and composition of RBCs. The role of RBCs is key to the investigation of many disease processes in various body systems. The size, shape variation, and distribution of RBCs can be used as clues to study pathologic processes and clinical diseases. EM has been used to reveal detailed structures of RBCs, including their pits, vacuoles, and the general organization of the infrastructure (the cytoskeleton network). Based on the advanced EM technologies, we are committed to assessing qualitatively and quantitatively RBC morphology, assisting in evaluating the structure and function of RBCs in humans and relevant disease processes.
Although white blood cells (WBCs) account for only about 1% of the volume of the blood, they assist to aid in the immune process and fight against various infections. WBCs come in different types, including monocytes, lymphocytes, eosinophils, neutrophils, and basophils. Based on our advanced EM technologies, researchers can identify WBCs and investigate their morphological changes in different conditions.
Platelets are another type of cell found in the blood and they are generally disk-shaped unless they become activated. As part of the blood, platelets prevent bleeding and help heal wounds by forming blood clots. Platelets are typically 2-5 µm in diameter, platelet granules are only 150-400 nm. At the iEM Platform, our advanced EM not only improves the resolution of the images but also the contrast, providing much clearer images. Platelet granules, including alpha and delta granules, can be visualized with sufficient clarity to allow accurate quantification and diagnosis.
Ultrastructural analysis of blood cells can be used to assist in the diagnosis of various diseases as well as basic and translational research. Creative Biostructure is an innovative, quality, and technology solution-driven company. Our advanced EM platform allows in-depth and comprehensive observation of various blood cells. If you are interested in our solutions, please feel free to contact us. We are always open to your questions and are happy to support you.
- Choudhary, O. P., et al. (2021). "Preparation of blood samples for electron microscopy: The standard protocol." Annals of Medicine and Surgery, 70, 102895.

