Adipocyte Imaging Using the iEM Platform
Adipose tissue (AT) is a main energy storage organ as well as an active endocrine organ, taking part in thermogenesis, control of the immune system, and neuroendocrine functions. In biology, function and structure are inexorably linked. The development of high-resolution electron microscopy (EM) has enhanced our understanding of adipocyte function.
Ultrastructural Features of Adipocytes
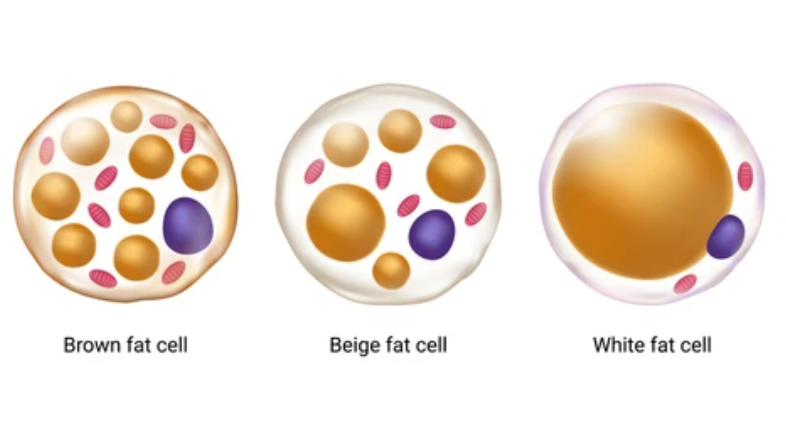
AT and is characterized by complex and highly active metabolism, and is composed of preadipocytes, mature adipocytes, adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs), adipose tissue macrophages (ATMs), stromal vascular fraction (SVF), T cells, and so on. Among them, adipocytes are the cells that primarily constitute adipose tissue. Based on the high-resolution electron microscopic techniques, such as transmission electron microscopy(TEM) and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), further identification and characterization of subcellular features of AT adipocytes can be achieved. Here, we show the ultrastructural characteristics of adipocytes, including white adipocytes, beige adipocytes, and bone marrow adipocytes.
| Ultrastructural Characteristics of Adipocytes | |||
| Ultrastructural Characteristics | White adipocyte | Beige adipocyte | Bone marrow adipocyte |
| Cytoplasm | Thin rim around lipid | Evenly distributed around lipid and organelles | Thin rim around lipid |
| Lipid | Large central unilocular droplet, smaller lipid droplets in cytoplasm | Small lipid droplets dispersed throughout cytoplasm | Large central lipid globule with smaller fat globules noted in the peripheral cytoplasm |
| Nucleus | Displaced toward the periphery, crescent or triangular shape. Peripheral chromatin condensation along the nuclear membrane and in association with nucleoli. | Centrally located. Peripheral chromatin condensation with a central euchromatic area and nucleolus. | Displaced toward the periphery, crescent or triangular shape. Peripheral chromatin condensation along the nuclear membrane and in association with nucleoli. |
| Mitochondria | Filamentous and spherical with rare, short, or gently wavy cristae. | Numerous, large mitochondria with closely packed, straight cristae. Increased mitochondrial volume (3.7-fold vs WAT). | Dense, usually spherical mitochondria. |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Mostly smooth ER | Cisternae of rough ER | Some profiles of rough ER |
| Surrounding matrix | Collagen-rich; adipocytes are "embraced" by a network of collagen fibers. | Vastly reduced collagenous matrix relative to WAT. | Lack of association with collagen, basal lamina positive for PAS and reticulin stains. |
Robles, H., et al, 2019.
Adipocyte Imaging at the iEM Platform
Creative Biostructure offers an integrated EM analysis, including SEM, and cryo-TEM analysis. We are dedicated to offering electron micrograph imaging of various adipocytes within their native microenvironment, including white adipocytes, beige adipocytes, and brown adipocytes. In addition to the basic ultrastructural features of adipocytes, we are also able to provide useful information on innervation, vasculature, and contacts between adipocytes. Moreover, adipose tissue-derived exosomes (AT-exosomes) have been demonstrated to take part in many physiologically and pathologically functions. These extracellular vesicles (EVs) are involved in the progression of many diseases and can be utilized for corresponding therapies. Our specific services include, but are not limited to, AT-exosome isolation, cryo-TEM observation, physiological and pathological function analysis of AT-exosomes.
Electron micrograph imaging of various adipocytes within their native microenvironment.
Electron micrograph imaging of mitochondria and other ultrastructural features of adipocytes.
Electron microscopy observation and identification of AT-exosomes.
Applications of Our Services
Identify different adipocyte types and their unique features at the high-resolution level.
Promote understanding of the subcellular and cellular mechanisms underlying adipocyte function.
Characterization of various adipocyte and adipose tissue in different diseases.
Improve the understanding of the communication between mammalian different tissues and organs through AT-exosome studies.
If you have questions concerning our services or you'd like to have some more information, you can contact us. We will be delighted to provide you with all the support we can to help establish a sustaining professional partnership.
Robles, H., et al. (2019). "Characterization of the bone marrow adipocyte niche with three-dimensional electron microscopy." Bone, 118, 89-98.
Zhao, R., et al. (2021). "Composition, isolation, identification and function of adipose tissue-derived exosomes." Adipocyte, 10(1), 587-604.

